Electric
Product Glossary
Use our Electric Powered Product Glossary to enhance your understanding of the terminology associated with our electric powered products.
Electric Powered Product Glossary
- Brake, Motor (Holding Brake): A friction brake for a hoist or trolley which is automatically applied and prevents motion when power is off.
- Brake, Weston: A mechanical brake that allows operation of the hoist to lift, lower, or move the load, and securely holds the load in between hoist operations.
- Bumpers: A device for reducing horizontal impact when a moving crane or trolley reaches the end of its permitted travel, or when two moving cranes or trolleys come into contact. This device may be attached to the bridge, trolley, or runway stop. Also referred to as buffers.
- Capacity: The maximum rated load a hoist is designed to lift. Also referred to as Working Load Limit (WLL) or Safe Working Load (SWL).
- Chain Container: Container that holds the ‘no-load’ side of the load chain. Can be made of canvas, plastic, or steel.
- Chain Fall Lines: The number of lines of chain between the hoist body and bottom hook. Also referred to as “reaves”, “falls”, or “parts”.
- Count Hour Meter: A device that records motor starts, running time and usage history by instant digital display. Integral to VFD on dual speed models.
- Drop Stops: A means to prevent an end truck or trolley from disengaging the beam or rail in the event of an axle or wheel failure.
- Emergency Stop (E-Stop): A red push button that stops all hoist and trolley function when pushed.
- Festooning: A method for supplying power and control. This method utilizes loops of cable suspended by a guide wire or enclosed track that traverses along with the hoist and trolley.
- Flange, Flat: A beam that has flat top and bottom flanges. Also referred to as “W” beams or “H” beams.
- Flange, Tapered: A beam that has tapered top and bottom flanges. Also referred to as “S” beams.
- Food Grade: A list of product options suitable for food processing/packaging applications. These may include items that are NSF compliant, as well as items that reduce corrosion.
- Friction Clutch: A device which prevents the hoist from damage due to over winding. Over winding is the event of the hook reaching and exceeding its upper or lower limit.
- Hand Chain (Geared Trolley): The chain that the operator pulls to traverse the load horizontally.
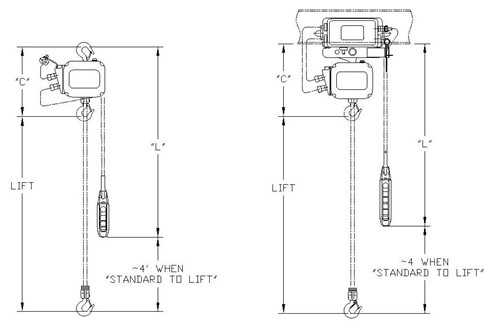
- Hand Chain Drop (Geared Trolley): On drawings in this catalog, hand chain drop is dimension ‘f’ for trolleys. Hand chain drop is a measure of how low the hand chain hangs. For a hoist suspended from a trolley, it is how low the hand chain hangs measured from the bottom of the beam that the trolley rides on.
- Headroom: On drawings in this catalog, headroom is indicated by dimension ‘C’. It is measured when the hoist’s bottom hook is in its uppermost position. For a hook-mounted hoist, headroom is the distance between the saddle of the top and bottom hooks. For a hoist suspended from a trolley, headroom is the distance from the bottom of the beam to the saddle of the bottom hook.
- Hoist Duty Service Classification Rating: A classification of hoist usage and service based on hours of operation and load. See specific product catalog for details on duty service classification.
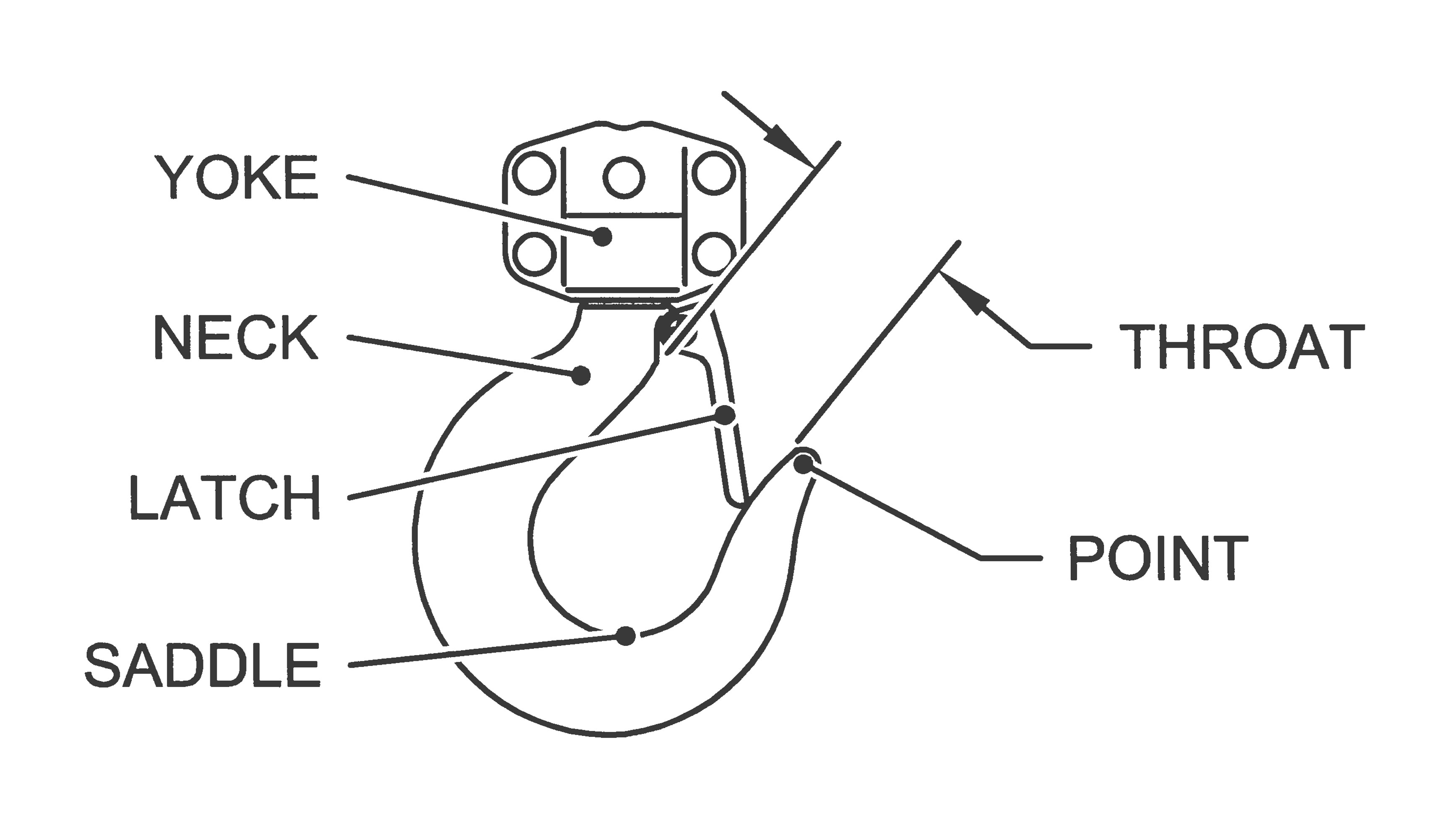
- Hook Parts:
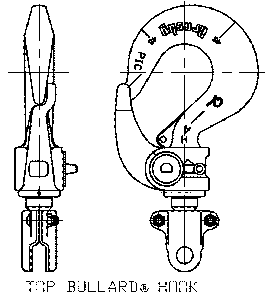
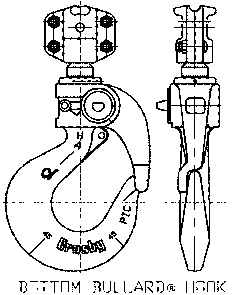
- Hooks, Bullard®: A hook with a positive locking, spring loaded gate.
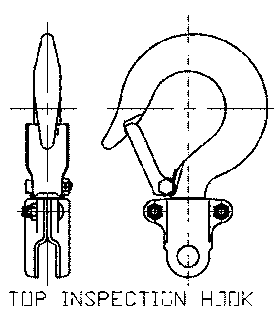
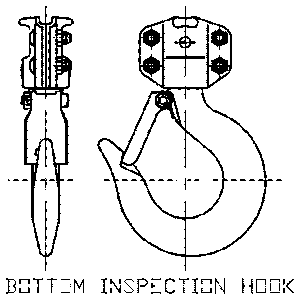
- Hooks, Inspection: Inspection hooks are suitable for applications where inspection of the internal parts of the hook set is required. The inspection hook uses the standard Harrington hook set and is assembled with high-strength locking fasteners instead of rivets.
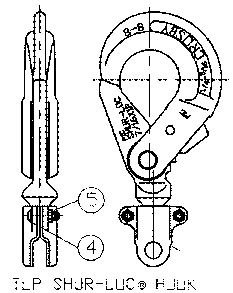
- Hooks, SHUR-LOC®: A hook with a positive locking latch that is self-locking and cannot be opened when hook is under load.
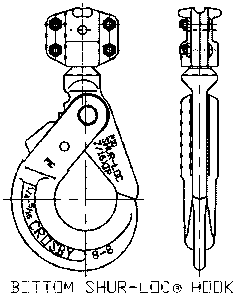
- Idle Sheave: Similar to a load sheave except for its location. Idle sheaves can be located in the upper or lower block and guides the chain as it reaves its way through the hook yoke(s).
- Infinitely Variable, 2-Step: An option available on some VFD controlled hoists and trolleys. 2 step infinitely variable allows the user to accelerate, then hold any speed between low and high.
- Infinitely Variable, 3-Step: Similar to 2-Step Infinitely Variable but also includes deceleration between high and low speed.
- Lift: The maximum vertical distance the bottom hook can travel.
- Load Chain: The hoist’s load bearing chain.
- Load Chain, Grade 80: Load chain used only on powered chain hoists, where the grade number indicates the relative strength of the chain for its size (i.e. larger grade numbers indicate stronger chain).
- Load Chain, Nickel Plated: Nickel Plated Load Chain: Load chain with an electroless nickel plating finish to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Load Sheave: The load chain fits into this specially designed sheave which drives the lifting and lowering of the hoist hook. Also referred to as load wheel or pocket wheel.
- Mechanical Load Brake: A mechanical brake that allows operation of the hoist to lift, lower, or move the load, and securely holds the load in between hoist operations. Also known as Weston Brake.
- Minimum Radius for Curve: Defines the sharpest curve of a beam on which the trolley can traverse.
- National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) Rating: A rating to show the application or environmental conditions enclosures are designed to protect against.
- Overload Limiter: A means to prevent the hoist from lifting damaging loads.
- Pawl: A component of the Weston brake that prevents rotation, thereby holding the load.
- Pendant: This is the hand held push button control device that is attached to the hoist or trolley. The number of buttons can vary dependently upon its uses.
- Pendant Drop: On drawings in this catalog, pendant drop is dimension ‘L’ for hoists and trolleys. Pendant drop is a measure of the distance the pendant hangs. For a hoist, it is the distance the pendant hangs from the hoist’s top hook. For a hoist suspended from a trolley, it is the distance the pendant hangs from the bottom of the beam that the trolley rides on. When pendant is specified as “standard to lift”, the bottom of the pendant will hang approximately 4’ above the bottom hook in its lowest position.
Hook Suspended Hoist / Trolley Suspended Hoist
- Plug and Play: A crane integration wiring method that terminates all crane wires and trolley hoist festooning via externally mounted plugs on the bridge control panel.
- Power, 3-Phase: A power supply consisting of 3 separate phases of AC Power and a ground, commonly used in industrial applications to power large motors and heavy loads. Common voltages include 208, 230, and 460.
- Power, Single-Phase: A power supply consisting of 1 phase of AC Power and a ground, commonly used in residential and light industrial applications. Common voltages include 115, 208, and 230.
- Smart Limits: An optional programmable upper and lower limit position feature available on dual-speed NER.
- Standard, ASME B30.16: “Safety Standard – Overhead Hoists (Underhung).”
- Standard, ASME B30.17: “Safety Standard – Cranes and Monorails (With Underhung Trolley or Bridge).”
- Standard, UL1340: “Standard for Safety, Hoists”.
- Suspender: A load bearing component designed to connect a hoist to a trolley. Also referred to as “lug”.
- Test Load: The load applied to the hoist to confirm proper operation in accordance with ASME B30.16 test requirements.
- Thermal Protection: A method to protect electric motors from damage due to over-current or overheating.
- Upper/Lower Limit Switches: An electro-mechanical device that prevents the lower hook from exceeding its’ limits of travel.
- Variable Frequency Drive (VFD): Also known as an inverter. An electronic device that controls the voltage and frequency to an electric motor to control speed and/or torque.